Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Treating Mental Health Disorders
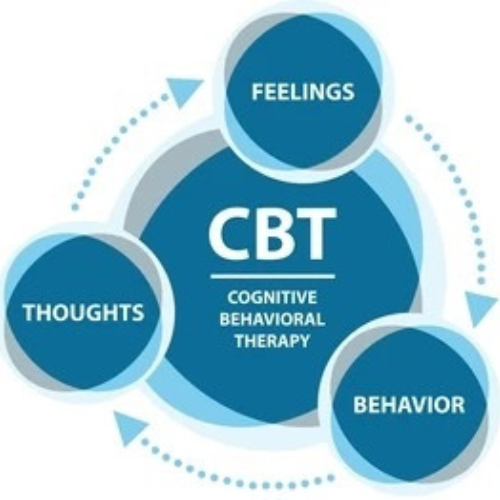
Cognitive behavioural therapy, or CBT, is a very successful, scientifically supported psychotherapy method that helps people identify and alter unhealthy thought, emotion, and behaviour patterns. CBT, which is based on the idea that our thoughts have a direct impact on our behaviour, offers organised methods for dealing with and overcoming a variety of mental health issues. This goal-oriented treatment is frequently used to treat PTSD, OCD, phobias, melancholy, anxiety disorders, and even problems like eating disorders and substance addiction. CBT gives people the skills they need to confront illogical ideas and change negative behavioural patterns, enabling them to become their own therapists.
Fundamentals of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy: Reorganising Cognitive Patterns
Maladaptive thinking causes negative feelings and self-destructive behaviours, which is the foundation of cognitive behavioural therapy. Through the recognition and modification of these cognitive distortions
- Recognize automatic thoughts
- Challenge irrational beliefs
- Develop healthier, balanced thinking
- Modify harmful behavioral patterns
Who Can Benefit from CBT?
It’s also an excellent tool for personal development, even in the absence of a clinical diagnosis. By improving thought patterns, CBT enhances decision-making, communication, and emotional well-being.
- Persistent sadness or hopelessness
- Excessive worry, fear, or panic
- Self-defeating behaviors
- Low self-esteem
- Irrational fears or phobias
- Interpersonal conflicts
- Trauma recovery
CBT in Treating Mental Health Disorders
Depression
CBT is considered a first-line treatment for depression. It helps patients identify negative thoughts such as “I am worthless” or “Nothing will ever get better” and teaches them to reframe these with realistic, positive alternatives. Through behavioral activation, clients are also encouraged to engage in activities that boost mood and energy.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
CBT enables individuals with GAD to recognize excessive worry patterns, understand their triggers, and utilize relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring to manage anxiety. Over time, this reduces avoidance behaviors and improves emotional regulation.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
CBT, particularly trauma-focused CBT (TF-CBT), helps survivors confront and reprocess traumatic memories. Techniques like exposure therapy and cognitive processing therapy are used to reframe the trauma, desensitize fear responses, and restore a sense of safety and control.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
In treating OCD, CBT integrates Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP). Patients are gradually exposed to obsessive thoughts while preventing compulsive behaviors, weakening the cycle of anxiety and compulsion.
Panic Disorder and Phobias
CBT helps clients confront feared situations through systematic desensitization and identify irrational fears. With repeated exposure and cognitive restructuring, individuals gain control over panic triggers and reclaim their lives.
